Hey there, networking enthusiasts! 🐍 Ready to crack open some knowledge on the CompTIA Network+ exam (N10-009)? Today, we’re covering the OSI Model and networking appliances—two key topics you’ll face on the exam. Let’s simplify these complex concepts, layer by layer, so you can crush the exam with confidence!
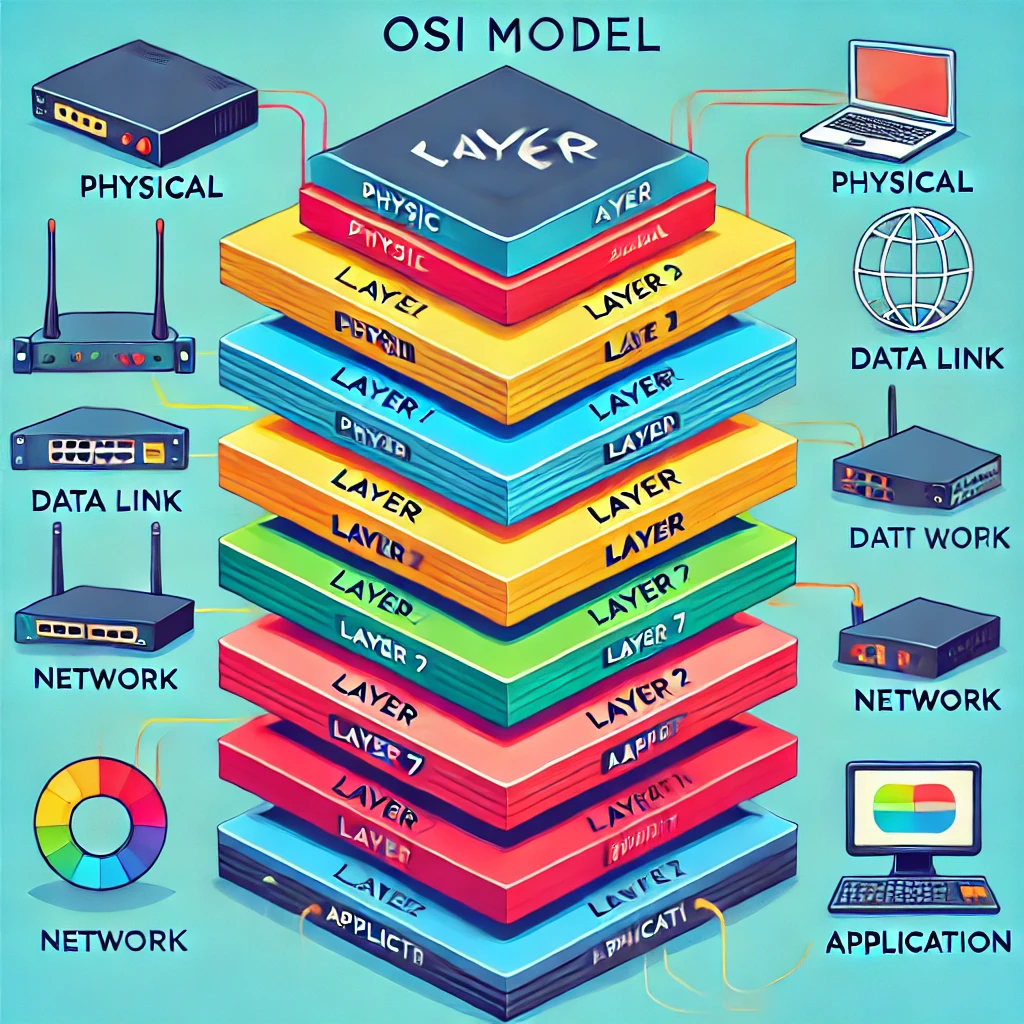
1️⃣ The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Reference Model
The OSI Model is like a networking cake 🎂 made up of 7 delicious layers, each with its own purpose in getting data from point A to point B. Think of it like a conversation at a dinner party; each layer has its role in making communication smooth.
Let’s break it down!
Layer 1: Physical – The Foundation of the Network 🛠️
- What it does: Defines the physical connection. Think of the cables, the signals, and the actual “plumbing” of the network.
- Example: Ethernet cables, fiber optics, and network interface cards (NICs).
Layer 2: Data Link – The Traffic Cop 🛑
- What it does: Manages node-to-node data transfer and handles MAC addresses (like car license plates on a network highway).
- Example: Switches, bridges, and the use of MAC addresses.
Layer 3: Network – The Navigator 🧭
- What it does: Responsible for moving data from one network to another. It’s the layer that works with IP addresses to route traffic.
- Example: Routers, IP addressing (IPv4, IPv6).
Layer 4: Transport – The Delivery Service 🚛
- What it does: Ensures complete data transfer. Think of this as the layer that delivers the entire package (data) and confirms delivery.
- Example: TCP (reliable, like FedEx) and UDP (faster but less reliable, like snail mail 🐌).
Layer 5: Session – The Conversation Starter 🎤
- What it does: Opens and closes sessions between devices. It makes sure the devices are “talking” properly during their communication session.
- Example: Managing video calls or file transfers.
Layer 6: Presentation – The Translator 🌐
- What it does: Converts data into a format the application can understand. Encryption and decryption also happen here.
- Example: SSL/TLS encryption, data format conversions (like JPEG, GIF).
Layer 7: Application – The Front Desk 💻
- What it does: This is where you, the user, interact with the network. It’s the “visible” layer, managing what apps use to communicate over the network.
- Example: Web browsers, email clients, FTP.
2️⃣ Networking Appliances, Applications, and Functions
Networking is like managing a big city full of intersections 🚦—you need the right devices and applications to keep traffic flowing smoothly. Let’s compare and contrast some key networking appliances and their functions.
Physical and Virtual Appliances 🏢 vs. 🖥️
- Physical Appliances: Hardware-based devices, like routers, switches, and firewalls, that physically exist in your network.
- Virtual Appliances: Software versions of these devices. They perform the same roles but in a virtualized environment (like in cloud networks).
Router 🛣️
- Directs traffic between different networks using IP addresses (Layer 3 device).
Switch 🎛️
- Connects devices within the same network and uses MAC addresses to direct traffic (Layer 2 device).
Firewall 🔥
- Monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules (acts like a security guard at the gate).
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)/Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) 🕵️♂️
- IDS: Detects suspicious activity (like a burglar alarm).
- IPS: Detects and stops suspicious activity (like a security system that blocks intruders).
Load Balancer ⚖️
- Distributes network traffic across multiple servers to ensure no one server is overwhelmed.
Proxy 🕶️
- Acts as an intermediary between a user and the internet, often for security or to manage traffic.
Network-Attached Storage (NAS) 🗄️
- A storage device connected to the network, allowing shared access to data (like a public filing cabinet).
Storage Area Network (SAN) 💽
- A dedicated network for data storage, usually for large enterprises needing high-performance storage solutions.
Wireless Access Point (AP) 📶
- Provides wireless network connectivity, allowing devices to connect to a wired network without using cables.
Controller 🕹️
- Manages multiple APs in larger wireless networks, ensuring smooth and efficient performance.
3️⃣ Networking Applications and Functions
Networking isn’t just about the appliances; functions and applications play a big role in keeping things running smoothly.
Content Delivery Network (CDN) 🚀
- A system of distributed servers that deliver web content to users based on their geographic location, improving load times.
Virtual Private Network (VPN) 🕵️♀️
- Extends a private network over a public one, allowing users to send and receive data securely as if their devices were directly connected to the private network.
Quality of Service (QoS) 🎯
- Ensures that high-priority traffic (like video calls or gaming) gets the bandwidth it needs to run smoothly, even when the network is busy.
Time to Live (TTL) ⏳
- Limits the lifespan of data in a network to prevent it from endlessly circulating. Kind of like an expiration date for packets.
Time to Test Your Knowledge! 🧠
Feeling ready to ace the CompTIA Network+ exam? Why not test your knowledge with a quick quiz? Head over to Kahoot and see how well you’ve mastered these concepts! 🏆